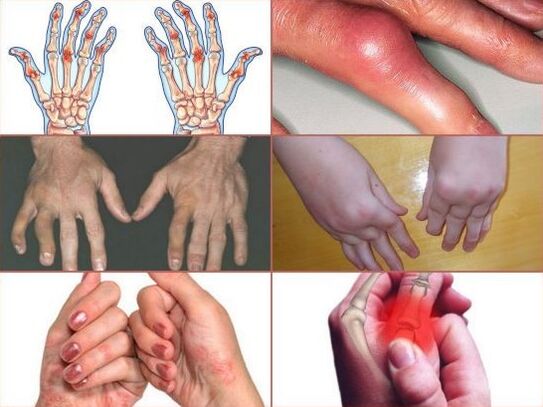
The hand is the most complex area of the upper limb in its structure. It consists of many bones closely grouped together. The bones are connected by 30 different joints - interphalangeal, metacarpophalangeal, carpometacarpal and radial.
According to statistics, hands are injured much more often than any other part of the body. Different injuries represent, according to various sources, from 30 to 50% of the total number of injuries of the musculoskeletal system and do not tend to decrease.
Therefore, of all the causes of pain in the fingers, the main one is trauma. In second place in terms of prevalence are connective tissue diseases - rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma and lupus erythematosus, psoriasis. Much less often the pain in the joints of the fingers is due to a violation of metabolic processes in gout, osteoarthritis.
Symptoms
The signs of non-traumatic injuries that may indicate the presence of joint pathology are the following:
- pain syndrome that is constant or wavy;
- pain when pressing and bending the fingers;
- swelling and redness of the skin above the joints;
- stiffness, stiffness during movements;
- deterioration of fine motor skills;
- squeaking, crunching and popping while bending the finger;
- the formation of subcutaneous nodules, painless to the touch;
- thickening of the skin in the folds;
- change in the configuration of the joints;
- increase in body temperature.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis most often affects the fingers and the right and left hands at the same time. This systemic disease is characterized by a malfunction in the immune system in which T lymphocytes begin to attack their own cells. The cells of the synovial membrane covering the joint capsule from the inside actively produce rheumatoid factors: pathological antibodies are protective protein molecules.
Rheumatoid factors then enter the bloodstream and bind to normal antibodies. As a result, immune complexes are formed, which settle on blood vessels and tissues. They are absorbed by the cells of the immune system - neutrophils and phagocytes, releasing substances that damage surrounding structures.
It is known that this is how inflammation develops in rheumatoid arthritis. However, scientists have not been able to determine the cause of this process. According to recent research in this area, the culprits for connective tissue damage are cytokines - signaling immune cells. Japanese experts have concluded that the study of this type of cells will help find an effective method of treatment.
In rheumatoid arthritis, each finger can hurt - index, middle, ring or small, but the lesion will always be bilateral. If one or more fingers of the left hand become ill, then the same fingers of the right hand begin to hurt almost immediately.
The phalanges in the area of the joints swell and redden due to the accumulation of fluid, do not bend well, especially in the morning. Morning stiffness can last up to 1 hour. Over time, the progression of arthritis leads to the replacement of smooth cartilage tissue with a fibrous structure, which disrupts the free movement of bones in the joint.
Gradually the joints become deformed, due to a change in the position of the joint elements, the pain intensifies. In the long course of the disease near the joints of the back of the hand appear small painless formations - rheumatoid nodules.
Psoriatic arthritis
The symptoms of this disease can resemble rheumatoid arthritis and appear on the background of dermatological pathology - psoriasis. In most cases, skin rashes appear first, and after a while the finger joints hurt.
Simultaneous manifestation of skin and joint lesions is possible, in 20 percent of patients the joints start to hurt earlier. Why psoriasis occurs is not known. It is thought to be triggered by genetic predisposition, immune system malfunction and infections. The average age of patients is 40 years.

Psoriatic arthritis can start, like rheumatoid arthritis, with general weakness and malaise, or it can manifest itself with acute pain sensations unexpectedly. Not only the toes but also the small joints of the feet, knees and shoulders can be affected. Participation in the pathological process can be both unilateral and symmetrical.
The pain syndrome is most pronounced at night and at rest. In the morning there is stiffness, during the day and with movements the pain subsides. Most often there is a lesion on one side - left or right and usually hurts not one but 2-4 joints (oligo-arthritis).
After a long rest, the fingers swell strongly and become like sausages, the tendons of the flexor muscles become inflamed, the skin above the joints acquires a purple-bluish tinge. The following symptoms indicate the presence of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis:
- red or pink scaly patches on the head, elbows, knees and thighs - can be single or cover a large area of skin;
- characteristic dimples on the skin of the hands, similar to smallpox, pigmentation of the fingers or toes;
- psoriatic plaques are hyperemic, edematous and may be itchy;
- joint pain is constant and does not pass during the day;
- mobility and functionality of the hand is significantly reduced.
The arthropathic form of psoriasis is one of the most severe. No deformity of the joints is usually observed, but if this occurs, then the fusion of the articular surfaces of the bones (ankylosis) is not excluded.
The danger of this disease is that the large joints and spine are gradually involved in the pathological process. Osteoporosis of the bones develops, the joints are destroyed, so psoriatic arthritis often leads to disability.
Osteoarthritis
In osteoarthritis, the process of formation of cartilage tissue covering the articular surfaces of the bones is disrupted. This is facilitated by both external and internal factors - trauma, high physical activity, hereditary predisposition and metabolic disorders.
Depending on the cause, osteoarthritis can be primary or secondary, developing against the background of endocrine or metabolic disease. Osteoarthritis most often affects the large joints of the lower extremities - knees, hips and ankles, as they carry the main load when walking and standing. Upper limbs are much less commonly affected.
When the fingers hurt due to prolonged exercise and after a break the pain disappears, the development of osteoarthritis is not excluded.
Over time, other symptoms appear:
- increased pain when clenching the fist or straining the fingers;
- increase in the size of the diseased joint;
- stiffness in the morning, requiring "development" of the fingers for 10-15 minutes or more;
- characteristic cracking when bending the fingers.
Osteoarthritis develops slowly and may not cause much anxiety for several years or even decades. However, in some cases there is a rapid increase in symptoms and a sharp deterioration of the condition. If at first the pain appears only during exertion, later it does not disappear even after rest.
Due to the marginal growths of the bones that form the joints, characteristic epiphyseal formations appear. Closer to the palm, Bouchard's nodules form in the proximal phalangeal joints. Next to the distal interphalangeal joints, located near the nails, are the Heberden nodes.
Stenotic ligamentitis
Stenotic ligamentitis affects the ligament-tendon apparatus of the hand and is manifested by blocking one of the fingers in a position of flexion or extension. The pathological process is caused by overload or excessive pressure on the ligament area, so the disease occurs among people engaged in manual labor - builders, welders, seamstresses and kitchen workers. In children, stenotic ligamentitis is extremely rare and affects only the thumb.
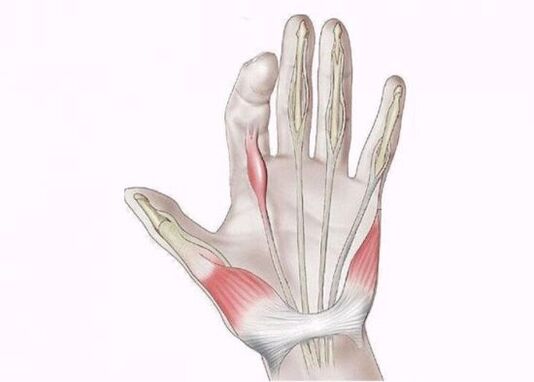
The main symptom of the disease is the "jumping" of the finger during elongation, accompanied by clicking. In the future, the "click" disappears and the finger remains motionless, turning into flexion or extensor contracture.
In the early stages, there is pain when pressing the palm at the base of the finger and difficulty in flexion / extension, especially in the morning. With a long course of ligamentitis you can move your finger only with the help of the other hand and after "clicking" there is pain that spreads not only to the palm but also to the forearm.
Which doctor to go to
In case of finger pain, you can first contact a therapist, who will refer you to a specialist - traumatologist, rheumatologist, hematologist, neurologist or surgeon. Clinical, radiation and laboratory methods of examination are used for diagnosis.
In order to determine the cause of the pain, pollination (history taking) and physical examination are performed, followed by X-ray or tomography, blood and urine tests.
Treatment
How to treat yourself and what to do next will depend on the results of the study. Task number 1 is to relieve pain and inflammation: for this prescribe drugs from the group of NSAIDs - nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. At present, a new generation of selective NSAIDs is being used more and more often.
Selective NSAIDs act selectively and have less toxic effects on the body, can be taken for a long time. If the pain syndrome is moderate or mild, topical agents are used - anti-inflammatory ointments and gels.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis includes basic and biological products, steroid hormones. These drugs suppress the immune system, thus reducing the intensity of the inflammatory process.
The same immunosuppressive drugs are prescribed if the joints hurt against the background of psoriatic arthritis. Methods such as plasmapheresis, chemisorption and photochemotherapy are used to reduce disease activity, prolong remission, and shorten the duration of drug therapy.
How to treat osteoarthritis of the joints depends on the stage of the disease. In stages 1-2, it is possible to significantly slow down the destruction of cartilage by taking chondroprotectors. Physiotherapy is effective, which enhances the effect of drugs and stimulates the recovery process.
For the treatment of osteoarthritis may be prescribed:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser;
- ultrasound;
- cryotherapy - exposure of joints with liquid nitrogen;
- balneotherapy - baths with mineral water;
- hirudotherapy - during treatment with leeches, substances that promote cartilage regeneration (hirudin, vitamins and hormones) enter the joint.
Therapeutic tactics in stenotic ligamentitis are determined taking into account the stage, the presence of provoking factors and the age of the patient. If the damage to the ligaments is minimal, it is recommended to reduce the load on the arm, if necessary, the arm is fixed with an orthosis or splint. In case of pain, anti-inflammatory drugs and hyaluronidase electrophoresis are prescribed.
Treatment of the second stage begins with conservative methods. The lack of effect for several months is an indication for surgery to cut the damaged joint. In patients with stage III conservative therapy is extremely rare, in most cases the operation is performed according to plan.
Note: due to the high risk of recurrence, it is very important to change your profession if it involves hand strain.
Folk remedies
Remedies prepared according to folk recipes can not be the main method of treatment, as they are not effective enough. However, as adjunctive therapy, such drugs will help relieve pain and enhance the effect of the drugs.

Mix a few bay leaves with juniper needles, add a little oil and massage your hands with the resulting ointment.
At night you can make a compress of crushed chalk, kefir, fermented baked milk or boiled oatmeal.
For compresses, green potatoes are used, which must be cut directly into the crust in a meat grinder or grater. Then immerse the mashed potatoes in hot water and heat to 39-40 °. Then put it in a linen bag and apply on inflamed joints for half an hour. The procedure can be done several times a day.
Paraffin applications relieve pain well if you put your hands in melted paraffin for 10 minutes and then keep them in each herbal decoction for 15-20 minutes. You can not be afraid of burns, because paraffin melts at a temperature not exceeding 65 °. 2-3 applications per week are enough to achieve the effect.
Bischofite compresses help accelerate tissue healing. Due to its composition, this natural mineral relieves pain and inflammation, restores joint mobility. Regular use of Bischofite maintains muscle and connective tissue tone.
It is recommended to make a compress with bischofite as follows: heat the joints with a heating pad or keep them in a warm bath, then rub bischofite, pre-diluted with water 1: 1, in the skin of the hands. The rubbing should last for a few minutes, after which a towel or gauze soaked in the solution is applied to the inflamed area. The top of the compress is covered with polyethylene and insulated. Bischofite compresses are made at night, in the morning hands are washed thoroughly with warm water. The procedure is performed every other day for three weeks.
Note: Bischofite compress can be applied to no more than three joints at a time.
The most important
To prevent or reduce the intensity of pain that has already occurred, you should keep the brushes warm and not expose them to hypothermia. Work that requires the same type of movement is best done intermittently, and when using vibrating tools, use gloves and hold the work brush with the other hand. When lifting and carrying heavy loads, the weight of the load must be evenly distributed on both limbs. You can also maintain healthy joints with proper nutrition, which should include foods containing calcium and omega-3 fatty acids.


















































